Fig. 4-2 The six bowels
Text
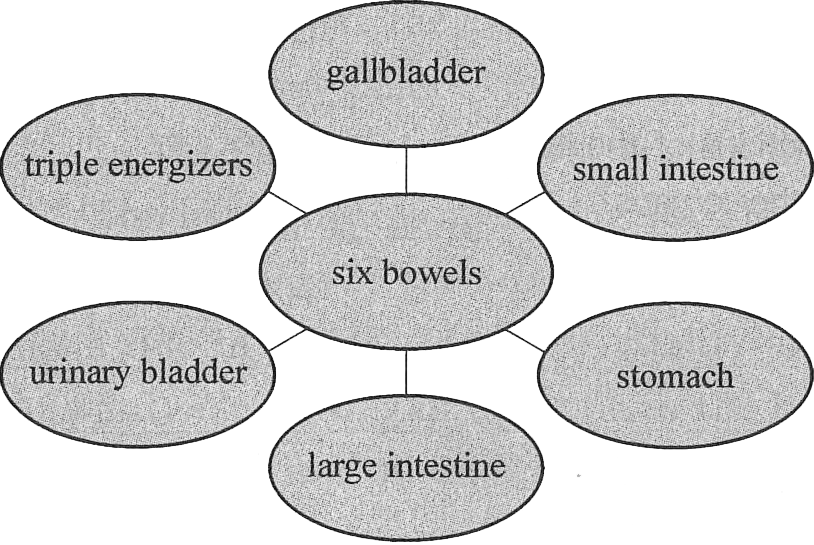
Six bowels is a general term for gall bladder, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, urinary bladder and triple energizers as listed in Fig. 4-2.

Fig. 4-2 The six bowels
Five viscera mainly manufacture and store essence and qi while six bowels mainly receive, transport and discharge things. Physiologically, six bowels govern downbearing. The stomach, small and large intestine alternately accept, transport and discharge food, the gallbladder stores and discharges bile and the urinary bladder stores and discharges urine. Again, because of space constraints, only the gallbladder will be discussed as an example. For further information on six bowels, you may check the following websites:
The gallbladder is one of the six bowels, which connecting with the liver, stores and discharges bile, and governs decision making. It forms an exterior-interior relation with the liver by the gallbladder meridian and liver meridian.
Bile is produced in the liver, and is secreted by the liver and then flows into the gallbladder for storage. During digestion, bile in the gallbladder is discharged into the intestinal tract by the free coursing function of the liver. Normal functions of the liver ensure proper bile formation, storage, excretion and discharge, so that normal digestive function is maintained. If the liver function is abnormal, the formation, excretion and discharge of bile will be inhibited, and the digestive function will be impaired.
The gallbladder helps people make judgments and decisions. This function of the gallbladder is also related to the liver, and the two cooperate to regulate mental and emotional activities. When they work in coordination, mental and emotional activities such as careful thinking, accurate judgment, firm determination, and normal seven emotions can be carried out normally.