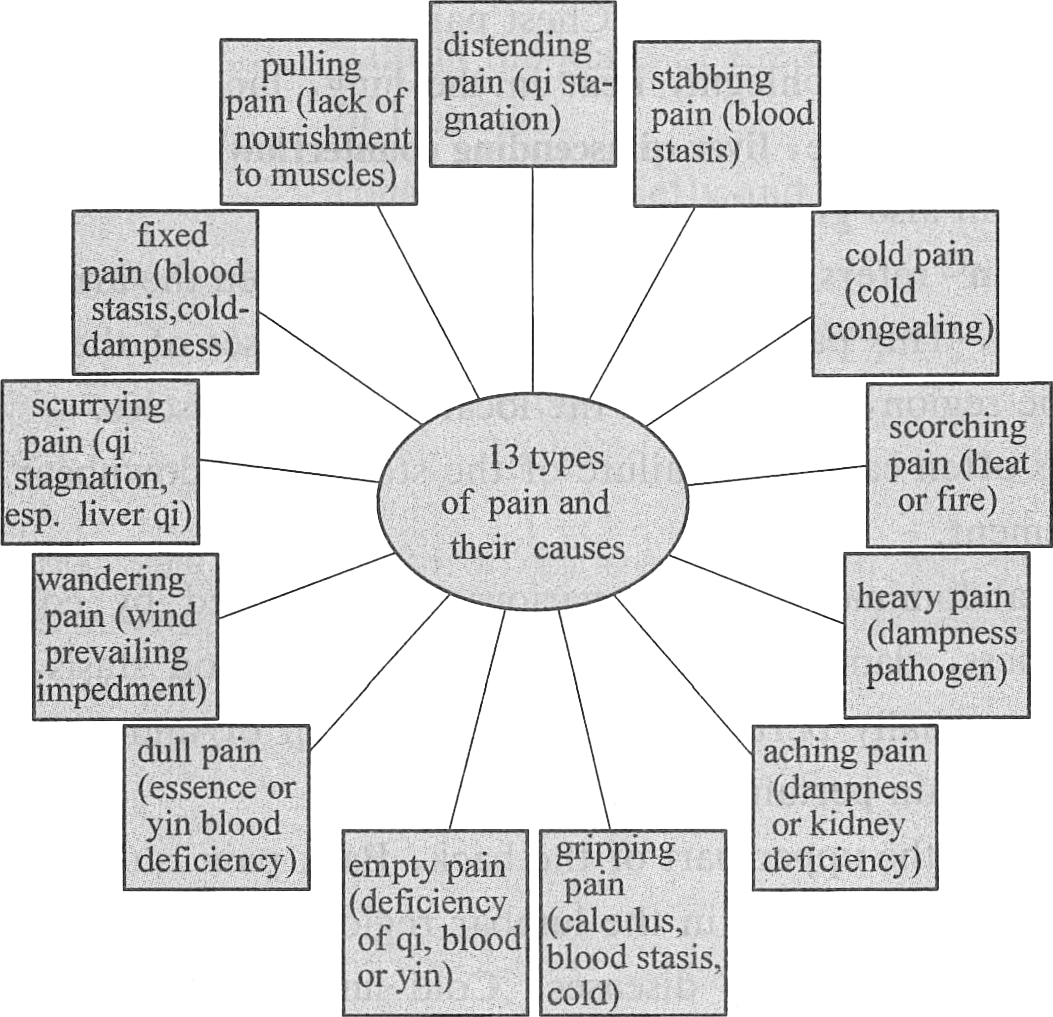
Fig. 8-2 Types of pain and their causes
Text
Pain is a very common subjective symptom and inquiry about pain includes inquiry about the location and nature of the pain.
Six excesses, qi stagnation, blood stasis, stagnation of phlegm, retained food, and worm accumulation can all cause excess pain, because they can cause stagnation to the meridians and vessels and prevent qi and blood from normal circulation.* "Stagnation leads to pain." Deficiency of qi, blood and yin essence can also cause pain because they can not nourish the body properly. "Deficiency leads to pain".
There are many types of pain and different pain arises from different mechanisms. Distending pain* usually indicates qi stagnation. However, distending pain in the head and eyes is usually seen in hyperactivity of liver yang or liver fire flaming upward. Stabbing pain* is a sign of blood stasis. Cold pain* often results from cold pathogen blocking the meridians, and can also be the result of yang qi deficiency. Scorching pain* refers to pain accompanied by a burning sensation, also called burning pain, usually caused by heat or fire, because heat and fire scorch. Heavy pain* is pain accompanied by a sensation of heaviness, usually caused by dampness pathogen. Aching pain* refers to a continuous dull pain as the sensation produced by prolonged physical exertion, mostly caused by dampness pathogen invading the muscle or joints, stagnating qi and blood movement. It can also be caused by kidney deficiency, and in this case, the pain is usually in the loins and knees as the kidneys are located in the loin region and govern the bones. Gripping pain* is an acute pain in the chest or abdomen. This pain mostly indicates localized excessive substantial pathogenic factors obstructing qi movement or cold pathogen obstructing qi movement. Empty pain* refers to a pain accompanied by a feeling of emptiness, often caused by debilitation of qi, blood and yin essence. Dull pain* is a continuous pain not stabbing in nature, which often appears in the head, chest, hypochondrium*, epigastrium* and abdomen. This pain mostly indicates essence and yin blood deficiency. Wandering pain* refers to a pain in the joints of the extremities with repeated change of location, usually observed in impediment disease*. Scurrying pain* refers to a pain that repeatedly changes location in the chest, hypochondrium, epigastrium and abdomen, and often indicates qi stagnation. Fixed pain* refers to a pain that is fixed in location. A fixed pain in the chest, hypochondrium, epigastrium or abdomen is often caused by blood stasis because blood is static in morbid condition; while fixed pain in the limbs and joints is often caused by cold and dampness because cold congeals and dampness is sticky.* Pulling pain* is a pain in one part involving other part (s), usually indicating lack of nourishment to the muscles and vessels or obstruction of qi and blood in the muscles and vessels, because a muscle or a vessel usually has two ends and connects two places. Fig. 8-2 summarizes the pain types with their causes.

Fig. 8-2 Types of pain and their causes
Severe pain, constant pain, pain in a new disease, or pain with refusal of pressure, is mostly excessive; while intermittent pain, mild pain, pain with preference for pressure, or pain in chronic disease is usually deficient.
The location of a pain is another important factor needs to be cleared when making a diagnosis. Headache can be a pain in a part of the head or the whole head. Headache caused by exterior pathogens (six excesses) is usually accompanied by the symptoms and signs of exterior pattern including fever, cold, sneezing and floating pulse. Phlegm, blood stasis, and worms can cause headache as they can obstruct or disturb the clear orifice (s). Headache of deficiency types is usually due to insufficiency of qi, blood, essence and marrow, since they fail to nourish the head when in deficiency. Headache caused by disease of local organs (nose, ears, eyes, teeth) is usually long term and associated with the symptoms and signs of the disease of the local organs. Liver diseases, including liver yang hyperactivity, liver fire flaming upward and liver fire invading the head, can all cause headache because liver yang or liver fire can bring excessive qi and blood to the head. Liver yin deficiency can also cause headache but due to liver yin deficiency failing to nourish the eyes and head. In this case, in addition to dizziness and blurred vision, the patient must also have dryness of the eyes, and thirst. Headache and dizziness, numbness and weakness of the limbs can be symptoms indicating the onset of wind stroke.
Chest pain is usually seen in heart and lung disease and some other conditions in TCM. Chest pain involved in heart disease is usually located in the heart region, in the interior part of the left arm or in the stomach region. Chest pain caused by lung disease is common and is usually the result of dryness, phlegm, heat in the lung, lung yin deficiency and liver fire invading the lung. Furthermore, liver qi ascending counterflow* and fluid retention in the chest and hypochondrium* can also give rise to chest pain.
Hypochondriac pain* refers to the pain in the area between the armpit and the lowest rib, unilateral* or bilateral. This pain is mostly related to diseases of the liver and gallbladder, fluid retention in the region, or injury of the local bones or muscles.
Stomach pain is often caused by failure of the stomach to downbear food and inhibition of stomach qi movement.
The causes of abdominal pain are various. Pain caused by cold congelation, heat binding, cold-dampness, dampness-heat, qi obstruction, blood stasis, food retention and parasite accumulation usually pertains to excess; while qi or /and blood deficiency, yin or yang deficiency caused pain pertains to deficiency.
Back pain is pain in the upper part of the back. Back pain is usually caused by injury of local sinews. Lumbago* means pain in the lumbar region. Weakness and soreness of the loins and knees* usually indicates kidney diseases. Cold lumbago aggravated in rainy weather usually indicates cold-dampness contraction. Aching lumbus can be caused by wind dampness obstructing the meridians in the lumbar region. Sudden and severe pain in lumber region involving the lower and lesser abdomen (groin region) indicates obstruction due to kidney stones or a stone in the ureter*. Additionally, strangury disease* is another reason that brings about lumbago. Limb pain* indicates diseases of the muscle, bones and joints of the limbs. And generalized pain* usually -indicates exterior pattern. However, generalized pain in prolonged disease may suggest qi or /and blood deficiency that fails to nourish the body.