
Fig. 15-4 The four basic types of purgative medicinals
Text
The four basic types of purgative medicinals are listed in Fig. 15-4. Offensive purgative medicinal* has a potent purgative effect for moving the bowels and driving away excessive heat and stagnant matter, such as dahuang (Radix et Rhizoma Rhei) and mangxiao (Natrii Sulfas).

Fig. 15-4 The four basic types of purgative medicinals
Purgative Medicinal*泻下药
Warm purgative medicinal* is a medicinal warm in property, which relieves constipation caused by excessive cold stagnation. Moistening purgative medicinal lubricates* the intestinal tract to facilitate defecation. Drastic (purgative) water-expelling medicinal* is a cathartic that causes copious water discharge for reducing accumulated fluid in the whole body, ascites and pleural* effusion.*
Digestant medicinals aid digestion and eliminate accumulated undigested food. Popularly used ones are shanzha (Fructus Crataegi), shenqu (Massa Medicata Fermentata), and maiya (Fructus Hordei Germinatus).
Worm-expelling* medicinals expel or kill parasitic worms, such as shijunzi (Quispualis Indica) and binglang (Areca*). Dampness-resolving medicinals are warm and dry with fragrant* odor, such as huoxiang (Medicinala Agastachis) and houpo (Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis).
Wind-dampness-dispelling medicinal is a category that dispels wind and dampness, mainly for relieving rheumatism* and related conditions, including wind-dampness-dispelling and cold-dispersing medicinal*, wind-dampness-dispelling and heat-clearing medicinal*, and wind-dampness-dispelling and sinew and bone-strengthening medicinal*.
Dampness-draining diuretic medicinals increase urine excretion and water discharge for treating internal retention of dampness. There are three subgroups: water-draining and swelling-dispersing medicinal*, strangury-relieving diuretic medicinal*, and dampness-draining anti-icteric medicinal*.
Qi-regulating medicinals regulate qi movement to treat qi stagnation or adverse qi flow. Interior-warming medicinals* warm the interior and expel internal cold.
Hemostatic medicinal* arrests bleeding, either internal or external. Blood-activating* and stasis-resolving* medicinal promotes blood flow and resolves blood stasis. Cough-suppressing and panting-calming medicinal relieves cough and dyspnea. Liver-pacifying and wind extinguishing medicinal pacifies the liver, suppresses exuberant yang, extinguishes internal wind and controls spasms or tremors. Orifice-opening medicinal is used for loss of consciousness in block pattern. Tonifying and boosting medicinal replenishes healthy qi and strengthens body resistance. And astringent medicinal arrests discharges.
Blood-activating medicinals are used in the treatment of retarded or static blood flow, and stasis-resolving medicinals are applied to the treatment of blood stasis, the types of which are listed in Fig. 15-5. Exterior-securing anhidrotic* medicinals can arrest excessive sweating by strengthening the superficies. Heat-clearing astringent medicinals can clear heat and check discharge; they are used in the treatment of bleeding or exudation* due to pathogenic heat. Lung-intestine astringent medicinals are sour and astringent and can relieve cough and dyspnea, and arrests chronic diarrhea. The other types of astringent medicinals are essence-securing*, urination reducing* and vaginal discharge checking* medicinals.
Worm killing and itch relieving medicinals are those that can kill worms and relieve itching, such as liuhuang (Sulphur), fengfang (Nidus Vespae), and shechuangzi (Fructus Cnidii).
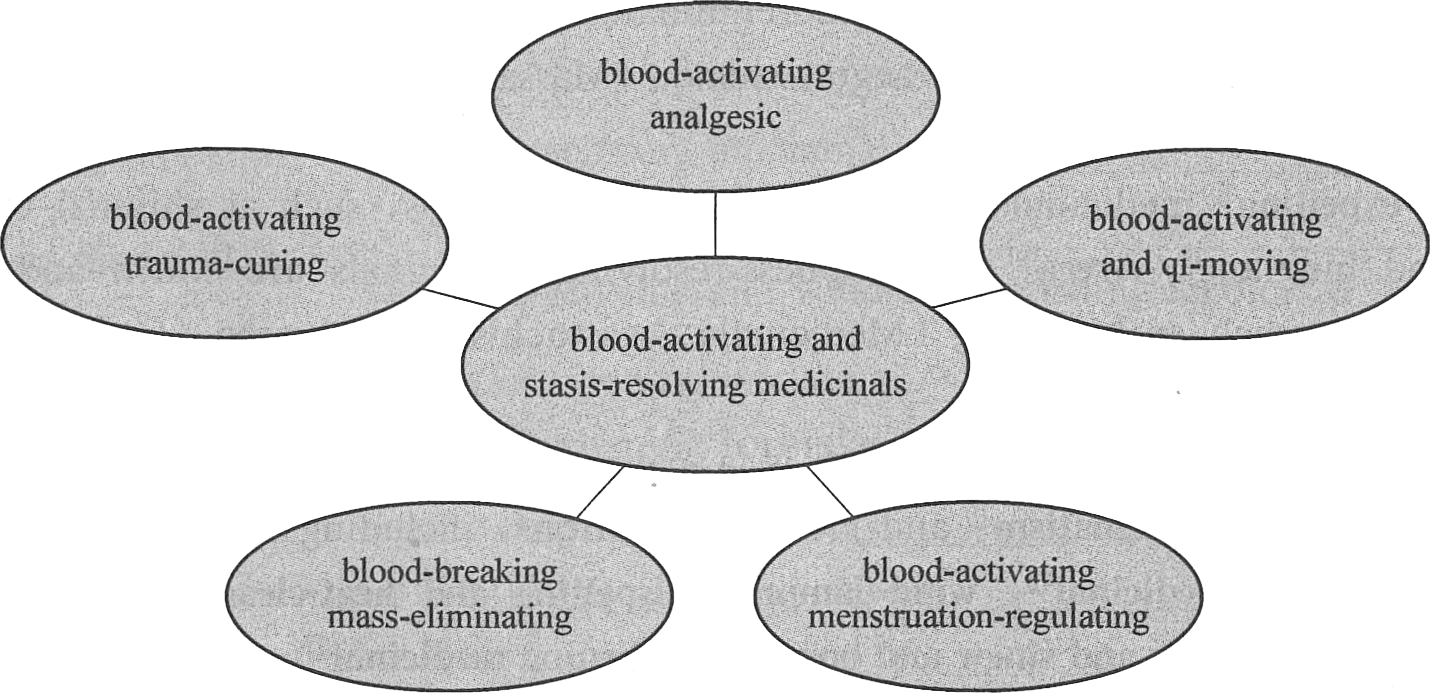
Fig. 15-5 Blood-activating and stasis-resolving medicinals